D-flat harmonic minor scale
The Solution below shows the Db harmonic minor scale notes, intervals and scale degrees on the piano, treble clef and bass clef.
The Lesson steps then explain how to identify the D-flat harmonic minor scale note interval positions, choose the note names and scale degree names.
For a quick summary to this topic, have a look at Harmonic minor scale.
| Key | C | C# | [Db] | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | A# | Bb | B | B# | Cb | All On 1 page |
|---|
Solution - 2 parts
1. D-flat harmonic minor scale
The D-flat harmonic minor scale has 1 double-flat, 5 flats.
Warning: The D-flat key is a theoretical harmonic minor scale key.
This means:
> Its key signature would contain either double-sharps or double flats.
> It is rarely used in practice, because it is too complex to use.
> It is not shown as a minor key on the Circle of fifths diagram, which contains the most commonly used minor keys.
> There is always an identical harmonic minor scale that you can use in its place, which is on the Circle of 5ths.
> The C# harmonic minor scale sounds the same / contains the same note pitches, which are played in the same order, and so it can be used as a direct replacement for the D-flat harmonic minor scale.
| Note no. | Note interval | Note name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tonic | The 1st note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Db |
| 2 | Db-maj-2nd | The 2nd note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Eb |
| 3 | Db-min-3rd | The 3rd note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Fb |
| 4 | Db-perf-4th | The 4th note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Gb |
| 5 | Db-perf-5th | The 5th note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Ab |
| 6 | Db-min-6th | The 6th note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Bbb |
| 7 | Db-maj-7th | The 7th note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is C |
| 8 | Db-perf-8th | The 8th note of the D-flat harmonic minor scale is Db |
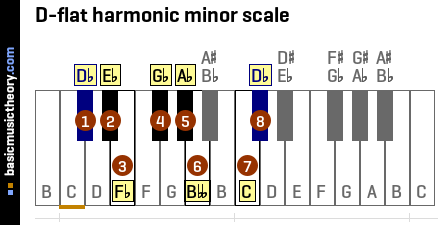
Middle C (midi note 60) is shown with an orange line under the 2nd note on the piano diagram.
These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef.
On the bass clef, Middle C is shown with an orange ledger line above the main 5 staff lines.

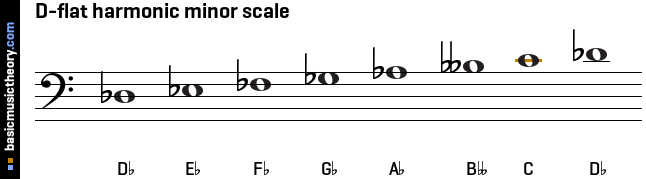
The stave diagrams above show the scale notes without a key signature, with the sharp / flat adjustments inserted before each note on the staff.
For the key signature of this scale, showing the symbols grouped correctly next to the bass or treble clef symbol at the beginning, have a look at the Db harmonic minor key signature.
| Note no. | Degree name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Db is the tonic of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 2 | Eb is the supertonic of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 3 | Fb is the mediant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 4 | Gb is the subdominant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 5 | Ab is the dominant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 6 | Bbb is the submediant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 7 | C is the leading tone of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 8 | Db is the octave of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
The difference between the D-flat harmonic minor scale and the Db natural minor scale is that the 7th note position of the minor scale is raised by one half-tone / semitone.
So whereas the Db natural minor scale has note Cb for the 7th note, this note is raised to arrive at note C for this harmonic minor scale.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
2. D-flat harmonic minor scale descending
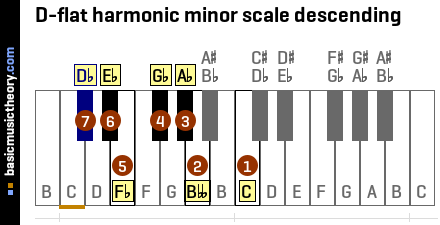


| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | C | Bbb | Ab | Gb | Fb | Eb | Db |
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
Lesson steps
1. Piano key note names
The white keys are named using the alphabetic letters A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, which is a pattern that repeats up the piano keyboard.
Every white or black key could have a flat(b) or sharp(#) accidental name, depending on how that note is used. In a later step, if sharp or flat notes are used, the exact accidental names will be chosen.
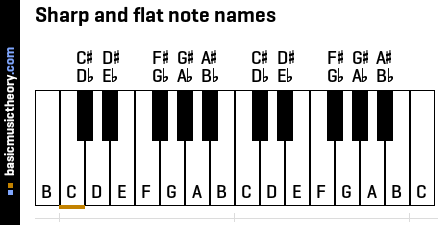
The audio files below play every note shown on the piano above, so middle C (marked with an orange line at the bottom) is the 2nd note heard.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
2. D-flat tonic note and one octave of notes
The numbered notes are those that might be used when building this note scale.
But since this is a scale in the key of Db, it is certain that notes 1 and 13 will be used in the scale.
Note 1 is the tonic note - the starting note - Db, and note 13 is the same note name but one octave higher.
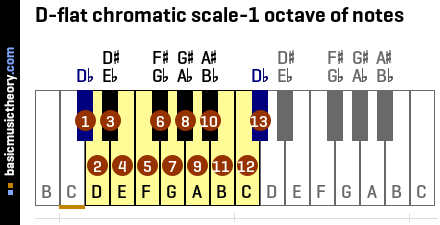
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Db | D | D# / Eb | E | F | F# / Gb | G | G# / Ab | A | A# / Bb | B | C | Db |
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
3. D-flat harmonic minor scale note interval positions
The harmonic minor scale uses the W-H-W-W-H-W½-H note counting rule to identify the scale note positions.
To count up a Whole tone, count up by two physical piano keys, either white or black.
To count up a Half-tone (semitone), count up from the last note up by one physical piano key, either white or black.
To count up a W½ tone (whole-tone and a half), count up from the last note by 3 half-tones / semitones - shown as 3 on the piano below.
The tonic note (shown as *) is the starting point and is always the 1st note in the harmonic minor scale.
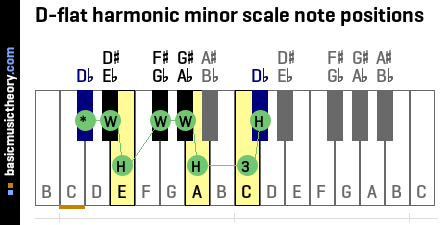
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Db | D# / Eb | E | F# / Gb | G# / Ab | A | C | Db |
What is the difference between the D-flat harmonic minor scale and the Db natural minor scale ?
The 7th note position (or scale degree) of the minor scale is raised by one half-tone / semitone to arrive at the harmonic minor scale note positions shown above, leaving a noticeably large interval of 3 half-tones / semitones between the 6th and 7th note positions for this scale.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
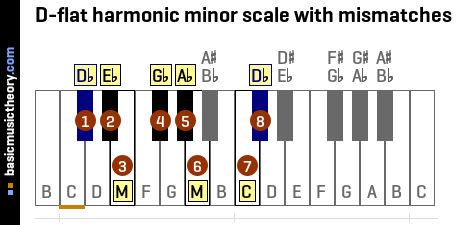
4. D-flat harmonic minor scale notes
The 7 unique notes in a scale need to be named such that each letter from A to G is used once only, so each note name is either a natural white name(A.. G) , a sharp(eg. F#) or a flat(eg. Gb).
This is needed to ensure that when it comes to writing the scale notes on a musical staff (eg. a treble clef), there is no possibility of having 2 G-type notes, for example, with one of the notes needing an accidental next to it on the staff (a sharp, flat or natural symbol).
To apply this rule, firstly list the white key names starting from the tonic, which are shown the White column below.
Then list the 7 notes in the scale so far, shown in the next column.
For each of the 7 notes, look across and try to find the White note name in the Scale note name.
If the natural white note can be found in the scale note, the scale note is written in the Match? column.
The 8th note - the octave note, will have the same name as the first note, the tonic note.
| No. | White | Scale note | Match? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D | Db | Db |
| 2 | E | D# / Eb | Eb |
| 3 | F | E | m |
| 4 | G | F# / Gb | Gb |
| 5 | A | G# / Ab | Ab |
| 6 | B | A | m |
| 7 | C | C | C |
| 8 | D | Db | Db |
For this scale, there are 2 mismatches (Shown as m in the Match? column), whose note names will need to be adjusted in the next step.
5. Make the D-flat note name adjustments
The adjustment explanation below needs to be applied to every mismatch m in the above table. The first mismatch is used as an example.
The match fails when trying to find a F-type of scale note, because either this type of note does not exist in this scale, or it exists but is in the wrong position number / table row for this match.
But music theory rules allow the name of any note to be sharpened or flattened, even white note names, so since a F-type of note name is needed, the real scale note Ewill be renamed to Fb.
Of course, even though the note is named Fb, when it comes to playing the note on an instrument, the real note E is really played.
The adjustments done in this step do not change the pitch / sound of the note, only the name of the note.
After doing the adjustments to all mistmatches, all letters A..G will have been used for this minor scale, and no rules have been broken.
Note that sometimes it is necessary to adjust the note name two half-tones / semitones forward or back, which will result in an adjusted name containing a double-sharp or double-flat.

| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Db | Eb | Fb | Gb | Ab | Bbb | C | Db |
6. D-flat harmonic minor scale descending
For harmonic minor scales, the notes names when descending are just the reverse of the ascending names.
So assuming octave note 8 has been played in the step above, the notes now descend back to the tonic.

| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | C | Bbb | Ab | Gb | Fb | Eb | Db |
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
7. D-flat harmonic minor scale degrees
Scale degree names 1,2,3,4,5,6, and 8 below are always the same for all major and minor scales (ie. 1st note is always tonic, 2nd is supertonic etc.) , but obviously the note names will be different for each scale / key combination.
In the harmonic minor scale, the 7th note is called the leading note or leading tone because the sound of the 7th note feels like it wants to resolve and finish at the octave note, when all scale notes are played in sequence.
It does this because in this scale, the 7th note is only 1 half-tone / semitone away from the 8th note - the octave note. The Db major scale and Db melodic minor scale scales share the same property - they both have only one half-tone / semitone between the 7th and 8th notes.
In contrast, the Db natural minor scale has a whole tone (two half-tones / semitones, two notes on the piano keyboard) between the 7th and 8th notes, and the 7th note does not lean towards the 8th note in the same way. In this case, the 7th note is called the subtonic.
| Note no. | Degree name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Db is the tonic of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 2 | Eb is the supertonic of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 3 | Fb is the mediant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 4 | Gb is the subdominant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 5 | Ab is the dominant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 6 | Bbb is the submediant of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 7 | C is the leading tone of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
| 8 | Db is the octave of the D-flat harmonic minor scale |
Related Keys and Topics
| Key | C | C# | [Db] | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | A# | Bb | B | B# | Cb | All On 1 page |
|---|