D-double-flat major 6th chord
The Solution below shows the D-double-flat major 6th chord in root position, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd inversions, on the piano, treble clef and bass clef.
The Lesson steps then explain how to construct this 6th chord using the 3rd, 5th and 6th note intervals, then finally how to construct the inverted chord variations.
For a quick summary of this topic, have a look at Sixth chord.
| Key | C | C# | Db | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | A# | Bb | B | B# | Cb |
|---|
Solution - 4 parts
1. D-double-flat major 6th chord
The D-double-flat major 6th chord contains 4 notes: Dbb, Fb, Abb, Bbb.
The chord spelling / formula relative to the Dbb major scale is: 1 3 5 6.
| Note no. | Note interval | Spelling / formula | Note name | #Semitones from root |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | root | 1 | The 1st note of the D-double-flat major 6th chord is Dbb | 0 |
| 2 | Dbb-maj-3rd | 3 | The 2nd note of the D-double-flat major 6th chord is Fb | 4 |
| 3 | Dbb-perf-5th | 5 | The 3rd note of the D-double-flat major 6th chord is Abb | 7 |
| 4 | Dbb-maj-6th | 6 | The 4th note of the D-double-flat major 6th chord is Bbb | 9 |
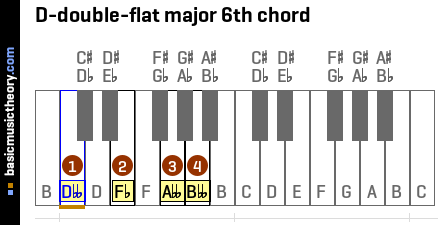
Middle C (midi note 60) is shown with an orange line under the 2nd note on the piano diagram.
These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef.

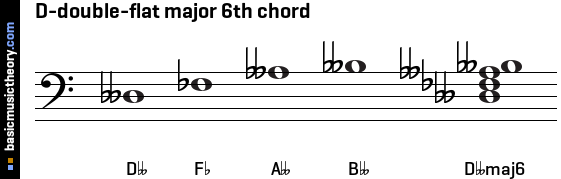
The figured bass symbols for this chord in root position are 6/5/3.
The staff diagrams and audio files contain each note individually, ascending from the root, followed by the chord containing all 3 notes.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
2. D-double-flat major 6th 1st inversion
The D-double-flat major 6th 1st inversion contains 4 notes: Fb, Abb, Bbb, Dbb.
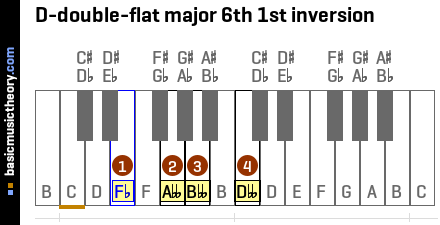
These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef.


The figured bass symbols for this chord in root position are 6/4/3, so the chord is said to be in six-four-three position.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
3. D-double-flat major 6th 2nd inversion
The D-double-flat major 6th 2nd inversion contains 4 notes: Abb, Bbb, Dbb, Fb.
These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef.


The figured bass symbols for this chord in root position are 6/4/2, so the chord is said to be in six-four-two position.
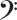 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
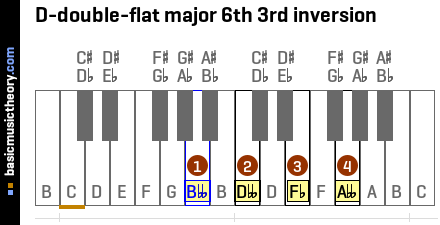
4. D-double-flat major 6th 3rd inversion
The D-double-flat major 6th 3rd inversion contains 4 notes: Bbb, Dbb, Fb, Abb.
These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef.


The figured bass symbols for this chord in root position are 7/5/3, so the chord is said to be in seven-five-three position.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
Lesson steps
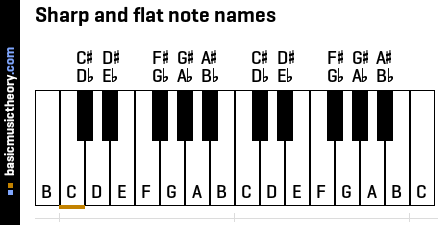
1. Piano key note names
The white keys are named using the alphabetic letters A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, which is a pattern that repeats up the piano keyboard.
Every white or black key could have a flat(b) or sharp(#) accidental name, depending on how that note is used. In a later step, if sharp or flat notes are used, the exact accidental names will be chosen.
The audio files below play every note shown on the piano above, so middle C (marked with an orange line at the bottom) is the 2nd note heard.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
2. D-double-flat tonic note and one octave of notes
The numbered notes are those that might be used when building this chord.
Note 1 is the root note - the starting note of the chord - Dbb, and note 13 is the same note name but one octave higher.
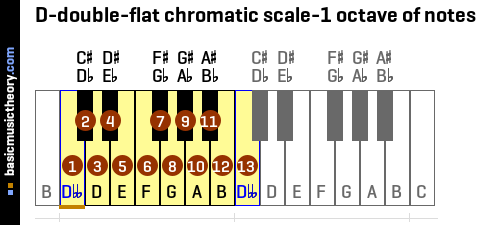
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Dbb | C# / Db | D | D# / Eb | E | F | F# / Gb | G | G# / Ab | A | A# / Bb | B | Dbb |
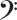 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
3. D-double-flat major scale note interval positions
The major scale uses the W-W-H-W-W-W-H note counting rule to identify the scale note positions.
To count up a Whole tone, count up by two physical piano keys, either white or black.
To count up a Half-tone (semitone), count up from the last note up by one physical piano key, either white or black.
The tonic note (shown as *) is the starting point and is always the 1st note in the major scale.
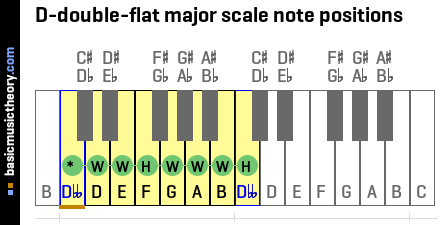
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Dbb | D | E | F | G | A | B | Dbb |
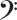 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
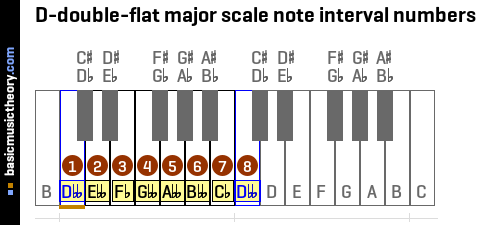
4. D-double-flat major scale note interval numbers
To identify the note interval numbers for this major scale, just assign each note position from the previous step, with numbers ascending from 1 to 8.
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Dbb | Ebb | Fb | Gbb | Abb | Bbb | Cb | Dbb |
To understand why the note names of this major scale have these specific sharp and flat names, have a look at the Dbb major scale page.
5. 6th chord qualities
6th chord definition
Whereas a triad chord contains 3 notes, a 6th chord contains 4 notes that are played together or overlapping.
6th chord qualities
Although others exist, the most common 6th chord qualities, are major, and minor.
Each chord quality name is the name of the entire chord as a whole, not its individual notes (which will be covered later).
Triad chords used for construction
Both major and minor chord qualities are built on the triad chord in the same key plus one added note - the 6th note of the major scale in the previous step.
So the D-double-flat major 6th chord is based on the Dbb major chord, and the D-double-flat minor 6th chord is based on the Dbb minor chord. The added 6th note in both cases is Bbb.
The steps below will detail the construction of the major 6th chord quality in the key of Dbb using note intervals.
6. 6th chord note intervals
Each individual note in a 6th chord can be represented in music theory using a note interval, which is used to express the relationship between the first note of the chord (the root note), and the note in question.
The root note is always the 1st note (note interval 1 in the above diagram) of the major scale diagram above. ie. the tonic of the major scale.
Then there is one note interval to describe the 2nd note, and another to describe the 3rd note of the chord, and finally another interval for the 4th chord note.
In the same way that the entire chord itself has a chord quality, the intervals representing the individual notes within that chord each have their own quality.
These note interval qualities could be diminished, minor, major, perfect and augmented.
Below is a table showing the note interval qualities for the most common 6th chords, together with the interval short names / abbrevations in brackets.
The final column shows the triad chord quality that the 6th chord is based on, so the 2nd and 3rd note quality columns are the same as the triad table for the same key.
| 6th chord quality | 2nd note quality | 3rd note quality | 4th note quality | Based on triad quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| minor | minor (m3) | perfect (P5) | major (M6) | minor |
| major | major (M3) | perfect (P5) | major (M6) | major |
The numbers in brackets are the note interval number (ie the scale note number) shown in the previous step.
Looking at the table above, the note intervals for the chord quality we are interested in (major 6th), in the key of Dbb are Dbb-maj-3rd, Dbb-perf-5th, and Dbb-maj-6th.
The links above explain in detail the meaning of these qualities, the short abbrevations in brackets, and how to calculate the interval note names based on the scale note names from the previous step.
7. D-double-flat major 6th chord in root position
Note name adjustments
Each note interval quality (diminished, minor, major, perfect, augmented) expresses a possible adjustment ie. a possible increase or decrease in the note pitch from the major scale notes in step 4.
If an adjustment in the pitch occurs, the note name given in the major scale in step 4 is modified, so that sharp or flat accidentals will be added or removed.
But crucially, for all interval qualities, the starting point from which accidentals need to be added or removed are the major scale note names in step 4.
For this chord, this is explained in detail in Dbb-maj-3rd, Dbb-perf-5th and Dbb-maj-6th, but the relevant adjustments for this major 6th chord quality are shown below:
Dbb-3rd: Since the 3rd note quality of the major scale is major, and the note interval quality needed is major also, no adjustment needs to be made. The 3rd note name - Fb, is used, and the chord note spelling is 3.
Dbb-5th: Since the 5th note quality of the major scale is perfect, and the note interval quality needed is perfect also, no adjustment needs to be made. The 5th note name - Abb is used, and the chord note spelling is 5.
Dbb-6th: Since the 6th note quality of the major scale is major, and the note interval quality needed is major also, no adjustment needs to be made. The 6th note name - Bbb is used, and the chord note spelling is 6.
If it is still not clear why the interval qualities are organised / related as they are, please refer to each of the interval links above.
D-double-flat major 6th chord note names
The final chord note names and note interval links are shown in the table below.
| Note | 1 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval No. | Dbb | Fb | Abb | Bbb |
| Interval def | root | Dbb-maj-3rd | Dbb-perf-5th | Dbb-maj-6th |
| Spelling | 1 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
| #Semitones | 0 | 4 | 7 | 9 |
The piano diagram below shows the interval short names, the note positions and the final note names of this triad chord.
In music theory, this 6th chord as it stands is said to be in root position because the root of the chord - note Dbb, is the note with the lowest pitch of all the chord notes.
The note order of this chord can also be changed, so that the root is no longer the lowest note, in which case the chord is no longer in root position, and will be called an inverted 6th chord instead.
For 6th chords, there are 3 possible inverted variations as described below.
Figured bass notation
The figured bass notation for a 6th chord in root position is 6/5/3, with the 6 placed above the 5, and the 5, above the 3.
These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord and the note in question.
So another name for this inversion would be D-double-flat major 6th triad in six-five-three position.
For example, the 6 represents note Bbb, from the Dbb-6th interval, since the chord root, Dbb, is the lowest note of the chord (as it is not inverted). .
In the same way, the figured bass 5 symbol represents note Abb, from the Dbb-5th interval, and the 3 symbol represents note Fb, from the Dbb-3rd interval
Since figured bass notation works within the context of a key, we don't need to indicate in the figured bass symbols whether eg. the 3rd is a major, minor etc. The key is assumed from the key signature.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
8. D-double-flat major 6th 1st inversion
To invert a chord, simply take the first note of the chord to be inverted (the lowest in pitch) and move it up an octave to the end of the chord.
So for a 1st inversion, take the root of the 6th chord in root position from the step above - note Dbb, and move it up one octave (12 notes) so it is the last (highest) note in the chord.
The second note of the original 6th chord (in root position) - note Fb is now the note with the lowest pitch.

Figured bass notation
The figured bass notation for this chord in 1st inversion is 6/4/3, with the 6 placed above the 4, and the 4 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram.
Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be D-double-flat major 6th triad in six-four-three position.
These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord (not necessarily the original chord root!), and the note in question.
For example, the 6 represents note Dbb, from the Fb-6th interval, since the lowest (bass) note of the chord - now inverted, is Fb.
In the same way, the figured bass 4 symbol represents note Bbb, from the Fb-4th interval, and the 3 symbol represents note Abb, from the Fb-3rd interval
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
9. D-double-flat major 6th 2nd inversion
For a 2nd inversion, take the first note of the 1st inversion above - Fb, and move it to the end of the chord.
So the second note of the 1st inversion - note Abb is now the note with the lowest pitch for the 2nd inversion.
Or put another way, the third note of the original 6th chord (in root position) is now the note with the lowest pitch.

Figured bass notation
The figured bass notation for this chord in 2nd inversion is 6/4/2, with the 6 placed above the 4, and the 4 placed above the 2 on a staff diagram.
Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be D-double-flat major 6th triad in six-four-two position.
These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord (not necessarily the original chord root!), and the note in question.
For example, the 6 represents note Fb, from the Abb-6th interval, since the lowest (bass) note of the chord - now inverted, is Abb.
In the same way, the figured bass 4 symbol represents note Dbb, from the Abb-4th interval, and the 2 symbol represents note Bbb, from the Abb-2nd interval
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
10. D-double-flat major 6th 3rd inversion
For a 3rd inversion, take the first note of the 2nd inversion above - Abb, and move it to the end of the chord.
So the second note of the 2nd inversion - note Bbb is now the note with the lowest pitch for the 3rd inversion.
Or put another way, the fourth note of the original 6th chord (in root position) is now the note with the lowest pitch.

Figured bass notation
The figured bass notation for this chord in 3rd inversion is 7/5/3, with the 7 placed above the 5, and the 5 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram.
Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be D-double-flat major 6th triad in seven-five-three position.
These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord (not necessarily the original chord root!), and the note in question.
For example, the 7 represents note Abb, from the Bbb-7th interval, since the lowest (bass) note of the chord - now inverted, is Bbb.
In the same way, the figured bass 5 symbol represents note Fb, from the Bbb-5th interval, and the 3 symbol represents note Dbb, from the Bbb-3rd interval
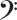 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
Related Keys and Topics
| Key | C | C# | Db | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | A# | Bb | B | B# | Cb |
|---|
| Related links | D-double-flat major 6th chord , Dbb, Dbb major scale |
|---|---|
| Minor scales | Dbb natural minor scale, Dbb harmonic minor scale, Dbb melodic minor scale |
| Intervals | Dbb-1st, Dbb-2nd, Dbb-3rd, Dbb-4th, Dbb-5th, Dbb-6th, Dbb-7th, Dbb-8th |
| Circle of 5ths | Learn the circle of fifths |
| Triad chords | Dbb diminished, Dbb minor, Dbb major, Dbb augmented, Dbb suspended 2nd, Dbb suspended 4th |
| 6th chords | Dbb minor 6th, Dbb major 6th |
| 7th chords | Dbb dim 7, Dbb half-dim7, Dbb min 7, Dbb min-maj 7, Dbb dom 7, Dbb maj 7, Dbb aug 7, Dbb aug-maj 7, Dbb maj 7 sus2, Dbb dom 7 sus4, Dbb maj 7 sus4 |
| 7th modes | ionian, C dorian, C phrygian, C lydian, C mixolydian, C aeolian, C locrian |
| Cadences | C major perfect authentic, C major imperfect authentic, C major plagal, C major half, C major deceptive |