A-sharp major perfect authentic cadence
The Solution below shows the A-sharp major perfect authentic cadence on the piano and treble clef.
The Lesson steps then describe the cadence structure in this key, the chords used, followed by an example of its use.
For a quick summary of this topic, have a look at Cadence.
| Key | C | C# | Db | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | [A#] | Bb | B | B# | Cb |
|---|
Solution
1. A-sharp major perfect authentic cadence
The perfect authentic cadence (PAC) moves from the dominant (V or V7), to the tonic (I) scale degree, with both chords in root position and the tonic being the highest note in chord I.
So in this major key for example, we are going from the A# major triad chord #V - E# major chord, to A# major triad chord #I - A# major chord.
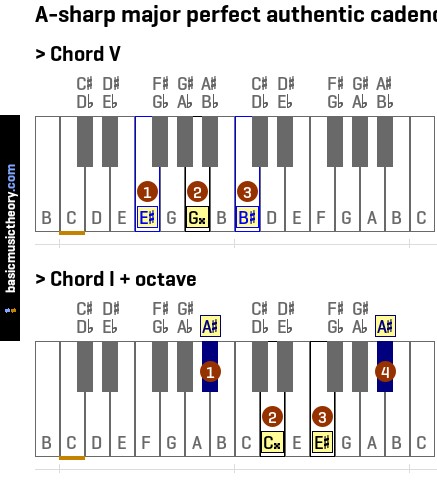

To demonstrate this, on the treble clef above, A# major triad chord #I, A# major triad chord #V, and A# major triad chord #IV are used to set up the phrase as being in this key, then the cadence chords V and I finish off the phrase, giving the sense of completion and finality characteristic of this cadence type.
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
Lesson steps
1. Cadence Types
Cadence definition
In music theory, a cadence is two chords which create a sense of closure, or rest to a phrase, section, or entire piece of music.
The most commonly used are: perfect authentic, imperfect authentic, plagal, deceptive and half cadence.
Some of the above are US-english terms. In the UK, authentic cadences are called perfect cadences, half cadences are called imperfect cadences, and deceptive cadences are called interrupted cadences.
Cadences - strong versus weak
Each of the above cadence types use different chords (or inversions) to create these rest / closure effects.
Strong cadences give a real sense of finality, and so are most often used right at the end of a piece.
In contrast, weak cadences are less conclusive, which can be used to create a sense of rest, or even surprise the listener with a false ending, when a strong cadence was expected in its place.
2. A-sharp major scale notes and chords
Before describing the details of the perfect authentic cadence in the key of A-sharp major, first it would be to useful to identify the scale notes, degrees and chords that could be used in this key.
A-sharp major scale notes
Below is a piano diagram showing the A# major scale notes.
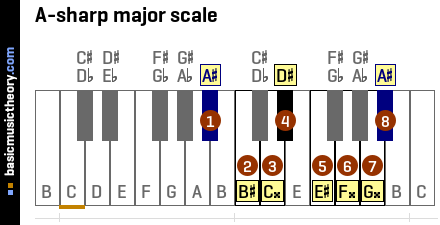
A-sharp major scale chords
For details on all the chords in this scale, have a look at A# major triad chords, and A# major 7th chords, but a summary table of all chord names and their scale degrees is shown below.
| Note no. | Note name | Scale degree | Triad chord # | 7th chord # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A# | tonic | A# major triad chord #I | A# major seventh chord #I7 |
| 2 | B# | supertonic | A# major triad chord #ii | A# major seventh chord #ii7 |
| 3 | C## | mediant | A# major triad chord #iii | A# major seventh chord #iii7 |
| 4 | D# | subdominant | A# major triad chord #IV | A# major seventh chord #IV7 |
| 5 | E# | dominant | A# major triad chord #V | A# major seventh chord #V7 |
| 6 | F## | submediant | A# major triad chord #vi | A# major seventh chord #vi7 |
| 7 | G## | leading tone | A# major triad chord #viio | A# major seventh chord #viiø7 |
For each note in the scale (2nd column), there is a triad chord whose root / first note is that scale note (4th column), and the same applies to 7th chords (5th column).
To understand what the roman numerals mean, please look at A# major triad chords or A# major 7th chords.
According to the cadence type, some of these chords, scale degrees and roman numerals will be used in later steps to define this cadence.
 Bass Clef
Bass Clef
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
3. A-sharp major perfect authentic cadence
Structure
An authentic cadence moves from the dominant (V or V7), to the tonic (I) scale degree.
So looking up the triad chords for these scale degrees from the table above, we are going from the A# major triad chord #V - E# major chord, to A# major triad chord #I - A# major chord.
Or if chord V7 is used in place of chord V, we move from the A# major seventh chord #V7 - E# dom 7 chord to the A# major chord. To keep things simple, we will use chord V from now on.
For an authentic cadence to be considered perfect, both of these chords need to be in root position, so on that count the links above are fine - both chords are in root position.
However, perfect cadences also need to have the tonic as the highest note of the tonic chord (I) - A# major chord. As you can see from this link, the tonic chord notes are currently A#, C##, and E#.
At the moment, the highest note of the I chord is E#, so to make this cadence perfect, we will add the octave of the tonic note into the chord. This is note 8 of the piano diagram in the above step, and as note 4 on the piano diagram below.

Example
The two chords above are shown as the last two chords on the treble clef below.
The first three chords on the staff below are not strictly part of the cadence, but they are useful to set the expectation that this phrase is definitely in the key of A-sharp major.
To do this, we are using chords A# major triad chord #I, A# major triad chord #V, and A# major triad chord #IV, and after hearing these chords, followed by the first chord in the cadence (V again), our ear is definitely expecting the tonic chord as the final chord in the sequence.
The 8th scale note on the final chord is the icing on the cake confirming that this is the perfect authentic cadence in action - we expected the end, and got it.

The audio files below also contain all 5 chords shown on the treble clef above.
 Treble Clef
Treble Clef
Related Keys and Topics
| Key | C | C# | Db | D | D# | Eb | E | E# | Fb | F | F# | Gb | G | G# | Ab | A | [A#] | Bb | B | B# | Cb |
|---|